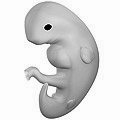
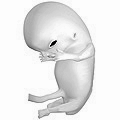
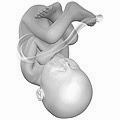
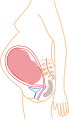
Prenatal development is divided into two primary biological stages. The first is the embryonic stage, which lasts for about two months. At this point, the fetal stage begins. At the beginning of the fetal stage, the risk of miscarriage decreases sharply,[36] all major structures including the head, brain, hands, feet, and other organs are present, and they continue to grow and develop. When the fetal stage commences, a fetus is typically about 30 mm (1.2 inches) in length, and the heart can be seen beating via sonograph; the fetus bends the head, and also makes general movements and startles that involve the whole body.[37] Some fingerprint formation occurs from the beginning of the fetal stage.[38]
Electrical brain activity is first detected between the 5th and 6th week of gestation, though this is still considered primitive neural activity rather than the beginning of conscious thought, something that develops much later in fetation. Synapses begin forming at 17 weeks, and at about week 28 begin to multiply at a rapid pace which continues until 3–4 months after birth. It is not until week 23 that the fetus can survive, albeit with major medical support, outside of the womb, because it does not possess a sustainable human brain until that time.[39]
Embryo at 4 weeks after fertilization[40] | Fetus at 8 weeks after fertilization[41] | Fetus at 18 weeks after fertilization[42] | Fetus at 38 weeks after fertilization[43] |
One way to observe prenatal development is via ultrasound images. Modern 3D ultrasound images provide greater detail for prenatal diagnosis than the older 2D ultrasound technology.[44] While 3D is popular with parents desiring a prenatal photograph as a keepsake,[45] both 2D and 3D are discouraged by the FDA for non-medical use,[46][dead link] but there are no definitive studies linking ultrasound to any adverse medical effects.[47] The following 3D ultrasound images were taken at different stages of pregnancy:
75-mm fetus (about 14 weeks gestational age) |
Some people are confused about the differences between an ultrasound and a sonogram. An ultrasound is the actual machine that lets you observe pregnancy. A sonogram is the image of the baby that the ultrasound produces. 4D Ultrasounds take 3D sonograms. Some people refer to the procedure as prenatal imaging, 3D imaging, a 3D scan, or 4D scan.
Physiological changes
During pregnancy, the woman undergoes many physiological changes, which are entirely normal, including cardiovascular, hematologic, metabolic, renal and respiratory changes that become very important in the event of complications. The body must change its physiological and homeostatic mechanisms in pregnancy to ensure the fetus is provided for. Increases in blood sugar, breathing and cardiac output are all required. Levels of progesterone and oestrogens rise continually throughout pregnancy, suppressing the hypothalamic axis and subsequently the menstrual cycle. The woman and the placenta also produce many hormones.
Managemen
Prenatal medical care is the medical and nursing care recommended for women before and during pregnancy. The aim of good prenatal care is to detect any potential problems early, to prevent them if possible (through recommendations on adequate nutrition, exercise, vitamin intake etc.), and to direct the woman to appropriate specialists, hospitals, etc. if necessary.
Nutritis
A balanced, nutritious diet is an important aspect of a healthy pregnancy. Eating a healthy diet, balancing carbohydrates, fat, and proteins, and eating a variety of fruits and vegetables, usually ensures good nutrition. Those whose diets are affected by health issues, religious requirements, or ethical beliefs may choose to consult a health professional for specific advice.
Adequate periconceptional folic acid (also called folate or Vitamin B9) intake has been proven to limit fetal neural tube defects, preventing spina bifida, a very serious birth defect. The neural tube develops during the first 28 days of pregnancy, explaining the necessity to guarantee adequate periconceptional folate intake.[48][49] Folates (from folia, leaf) are abundant in spinach (fresh, frozen, or canned), and are found in green leafy vegetables e.g. salads, beets, broccoli, asparagus, citrus fruits and melons, chickpeas (i.e. in the form of hummus or falafel), and eggs. In the United States and Canada, most wheat products (flour, noodles) are fortified with folic acid.[50]
DHA omega-3 is a major structural fatty acid in the brain and retina, and is naturally found in breast milk. It is important for the woman to consume adequate amounts of DHA during pregnancy and while nursing to support her well-being and the health of her infant. Developing infants cannot produce DHA efficiently, and must receive this vital nutrient from the woman through the placenta during pregnancy and in breast milk after birth.[51]
Several micronutrients are important for the health of the developing fetus, especially in areas of the world where insufficient nutrition is prevalent.[52] In developed areas, such as Western Europe and the United States, certain nutrients such as Vitamin D and calcium, required for bone development, may require supplementation.[53][54][55]
Dangerous bacteria or parasites may contaminate foods, particularly Listeria and toxoplasma, toxoplasmosis agent. Careful washing of fruits and raw vegetables may remove these pathogens, as may thoroughly cooking leftovers, meat, or processed meat. Soft cheeses may contain Listeria; if milk is raw, the risk may increase. Cat feces pose a particular risk of toxoplasmosis. Pregnant women are also more prone to Salmonella infections from eggs and poultry, which should be thoroughly cooked. Practicing good hygiene in the kitchen can reduce these risks.[56]
Weight gain
Caloric intake must be increased to ensure proper development of the fetus. The amount of weight gained during a single pregnancy varies among women. The Institute of Medicine recommends an overall pregnancy weight gain for women starting pregnancy at a normal weight, with a body mass index of 18.5-24.9, of 25-35 pounds (11.4-15.9 kg).[57] Women who are underweight, with a BMI of less than 18.5, may need to gain between 28-40 lbs. Overweight women are advised to gain between 15-25 lbs, whereas an obese woman may expect to gain between 11-20 lbs. Doctors and dietitians may make different, or more individualized, recommendations for specific patients, based on factors including low maternal age, nutritional status, fetal development, and morbid obesity.
During pregnancy, insufficient or excessive weight gain can compromise the health of the mother and fetus. All women are encouraged to choose a healthy diet regardless of pre-pregnancy weight. Exercise during pregnancy, such as walking and swimming, is recommended for healthy pregnancies. Exercise has notable health benefits for both mother and baby, including preventing excessive weight gain.[58]
Immune tolerance
The fetus inside a pregnant woman may be viewed as an unusually successful allograft, since it genetically differs from the woman.[59] In the same way, many cases of spontaneous abortion may be described in the same way as maternal transplant rejection.[59]
Medication use
Drugs used during pregnancy can have temporary or permanent effects on the fetus. Therefore many physicians would prefer not to prescribe for pregnant women, the major concern being over teratogenicity of the drugs.
Drugs have been classified into categories A,B,C,D and X based on the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) rating system to provide therapeutic guidance based on potential benefits and fetal risks. Drugs like multivitamins that have demonstrated no fetal risks after controlled studies in humans are classified as Category A. On the other hand drugs like thalidomide with proven fetal risks that outweigh all benefits are classified as Category X.[60]







Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar